It’s likely that you’ve heard of probiotics, but what are prebiotics? There’s quite a bit of discussion going on about prebiotics vs probiotics, and which is better for digestive health.
The term prebiotics has been around since 1995, when it was introduced by two scientists at Cambridge university in England. However, although prebiotics are growing in popularity as a natural digestive, many people still haven’t heard of them.
Simply put, prebiotics are non digestible foods, typically carbohydrates, that feed good bacteria in the digestive system in a way that’s beneficial for health.
However, scientifically, the prebiotics definition is a little more complicated than that. It’s also been refined since it was first established.
The initial study classified prebiotics as a “non-digestible food ingredient that beneficially affects the host by selectively stimulating the growth and/or activity of one or a limited number of bacteria in the colon, and thus improves host health”.
In 2004, the concept was reviewed and the prebiotics definition amended to be “a selectively fermented ingredient that allows specific changes, both in the composition and/or activity in the gastrointestinal microbiota that confers benefits upon host wellbeing and health.”
The aim was to address concerns that foods were being labeled as having a prebiotic effect without considering clear criteria. This is:
- resistance to gastric acidity, hydrolysis by mammalian enzymes and gastrointestinal absorption;
- fermentation by intestinal microflora; and
- selective stimulation of the growth and/or activity of intestinal bacteria (particularly bifidobacteria and/or lactobacilli) associated with health and wellbeing.
Common Prebiotic Compounds
Two of the most highly researched and widely accepted prebiotic compounds are types of oligosaccharides called inulin and oligofructose (a sub group of inulin). They’re made up of chains of glucose and fructose (fruit sugar). Most commercial inulin is extracted from chicory root. Jerusalem artichokes are also high in inulin. Other sources are onions, leeks and garlic.
In 2002, this study confirmed that inulin and oligofructose were both particularly effective prebiotics. They resisted digestion in the upper gastrointestinal tract, enabling them to reach the large intestine where they were fermented by the “good bacteria”.
Kiwi Fruit – An Emerging Prebiotic
Initially, scientists thought that oligosaccharides were the main prebiotics. However, as research into prebiotic compounds and what goes on in the colon has continued, a whole new range of prebiotic compounds has emerged.
One of the most interesting studies, conducted by the New Zealand Institute of Plant & Food Research and published in 2010, found that the pectin (insoluble fiber in plant cell walls) in kiwi fruits displayed better prebiotic activity than inulin.
The tests revealed that the pectin greatly enhanced the adhesion of “good bacteria” Lactobacillus rhamnosus to the intestinal epithelial cells, more so than inulin. It also helped the body fend off bacterial invasions by decreasing the adhesion of “bad bacteria” Salmonella typhimurium.
A Powerful Prebiotic Kiwi Fruit Supplement
Wouldn’t it be great if you could take a kiwi fruit supplement and get such a beneficial prebiotic effect?
Fortunately, you can. Only one capsule a day is necessary. And, it’s less costly than eating kiwi fruits.
The supplement is a remarkable new product called Kiwi Klenz. Unlike other similar supplements, it’s not made out of dried kiwi fruit. Kiwi Klenz is a potent extract of both the kiwi fruit skin and pulp.
Impact of Kiwi Klenz on Good Bacteria
Laboratory data has shown Kiwi Klenz to have the following beneficial prebiotic effect on the good bacteria in the colon.
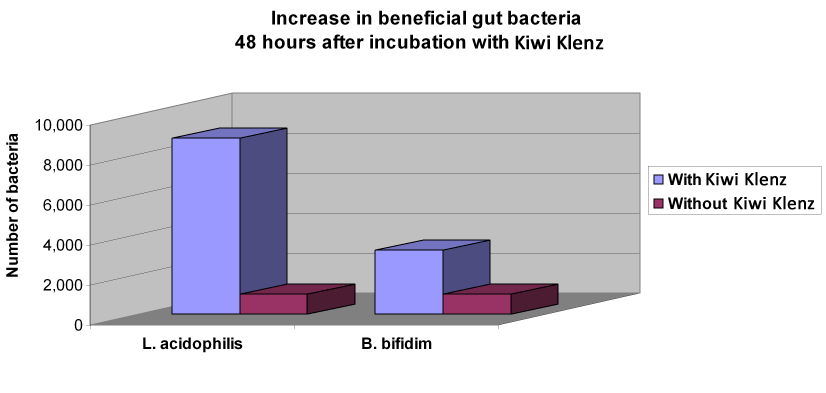
While this is extremely helpful for intestinal health, Kiwi Klenz also contains other important nutrients (enzymes and phenolics) that are essential for good digestion. Find out about the 5 Health Benefits of Kiwi Fruit for Digestion.
If you’re thinking of trying Kiwi Klenz (and you should, because there’s no other natural digestive product like it on the market), the great thing is that you can do it completely RISK FREE!
GET RESULTS WITHIN 30 DAYS OR A FULL REFUND OF YOUR MONEY!
Find out what customers have to say about Kiwi Klenz in these customer comments



